Storage
MolnOS Storage provides a simple, S3-like object storage system for files, documents, media, and any binary data. Organize objects in buckets with hierarchical folder-like navigation using prefixes.
Features
Section titled “Features”Bucket Management
Section titled “Bucket Management”Create and manage storage buckets to organize your objects. Each bucket is an isolated container with its own namespace.
Object Upload & Retrieval
Section titled “Object Upload & Retrieval”Store and retrieve objects of any type - text files, images, videos, JSON documents, and binary data. Supports multiple upload methods:
- JSON upload for text content
- Binary upload with query parameters
- Multipart form upload for file uploads
Hierarchical Navigation
Section titled “Hierarchical Navigation”Navigate objects using S3-style prefix filtering. The system creates virtual folders from common prefixes, allowing you to browse storage like a traditional file system while maintaining the simplicity of a flat key-value structure.
Object Metadata
Section titled “Object Metadata”Each object includes metadata: size, last modification time, and type (file or folder). Track when objects were created and how much space they consume.
Bucket Statistics
Section titled “Bucket Statistics”View bucket-level statistics including total object count and total storage size.
Common Use Cases
Section titled “Common Use Cases”- User Uploads: Store profile pictures, documents, and user-generated content
- Static Assets: Host images, videos, and media files for web applications
- Backups: Store database backups, configuration snapshots, and archives
- Log Archives: Archive old log files and audit trails
- Document Management: Organize and store business documents, contracts, and files
- CDN Origin: Use as origin storage for content delivery networks
- Data Lake: Store raw data for analytics and processing pipelines
How It Works
Section titled “How It Works”Console
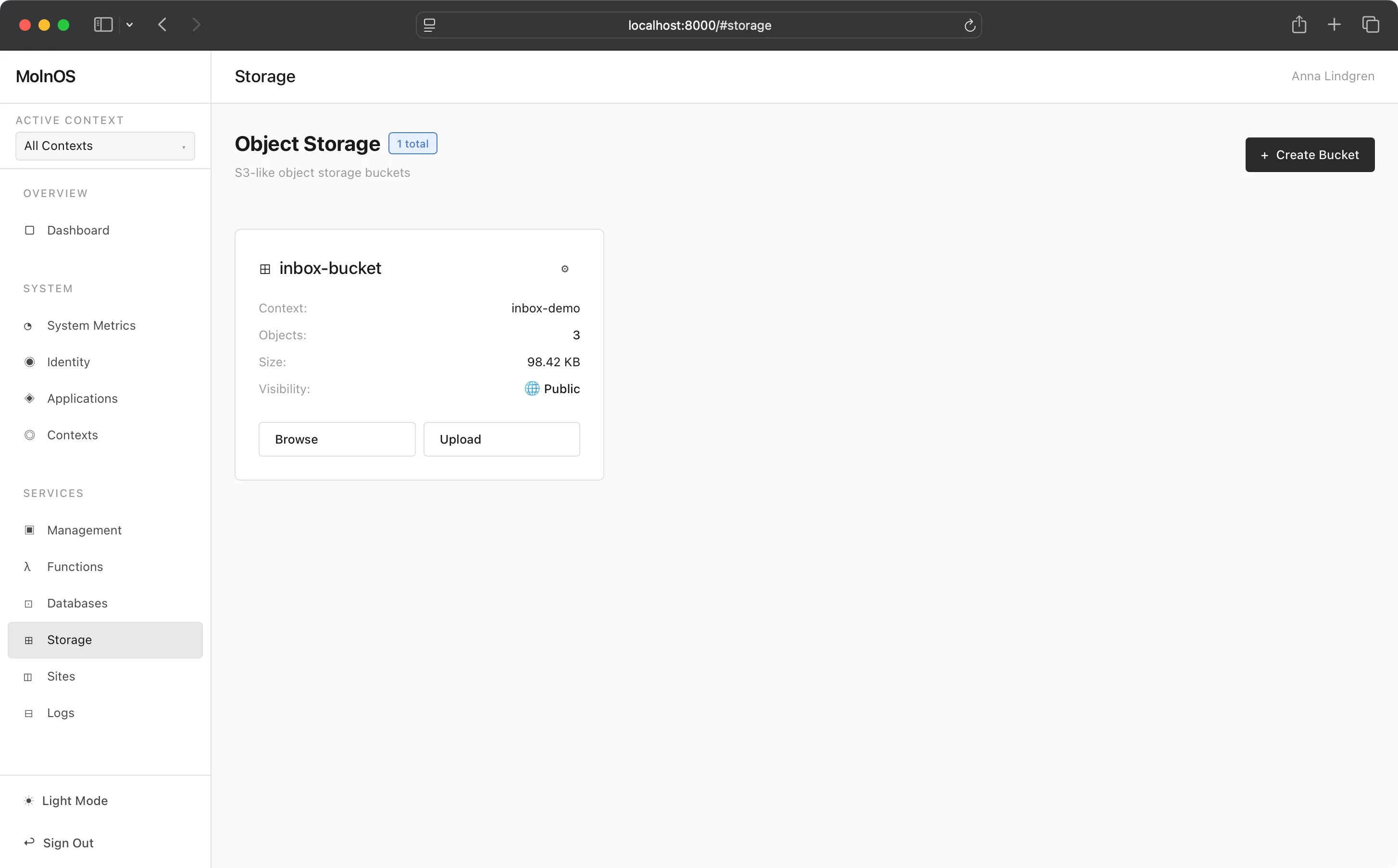
Section titled “Console”You can create both public and private buckets in MolnOS. To create a bucket, just click the button, add the bucket a name, decide if the bucket should be public or not, and you are done.
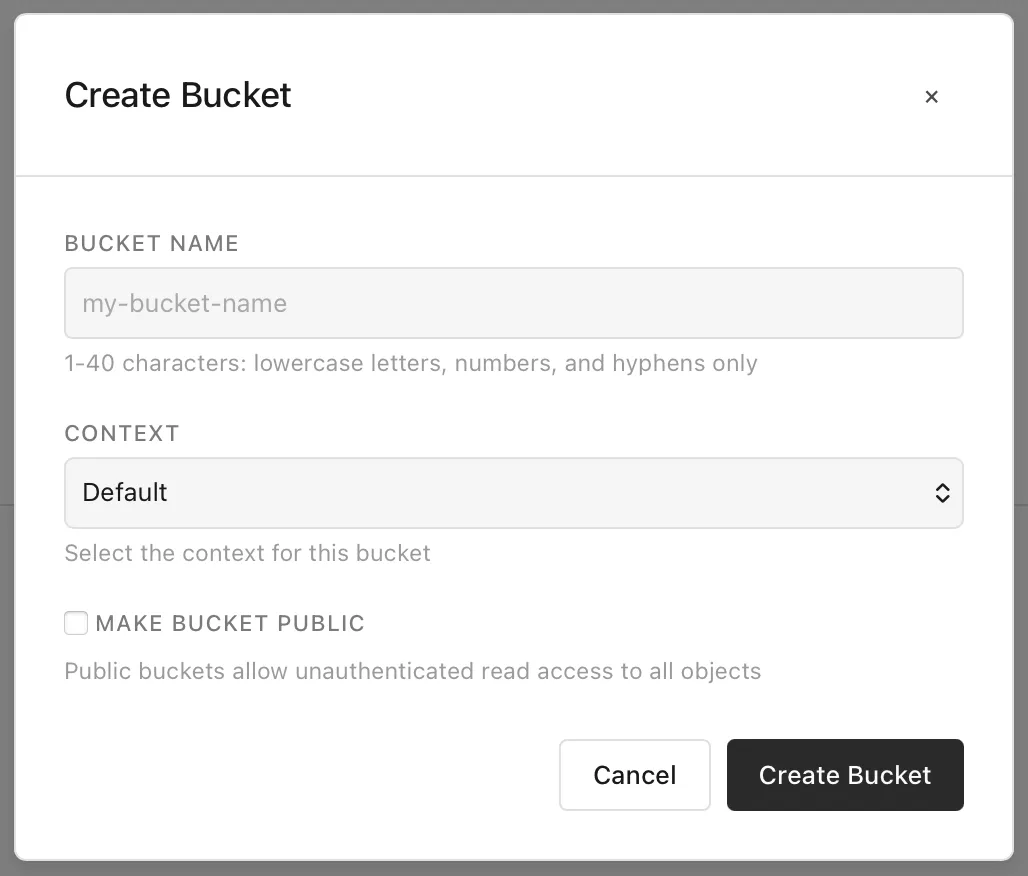
To upload a file (or more), select them and add an optional path. If not providing a path, files will be created relative to the current “location” in the bucket.
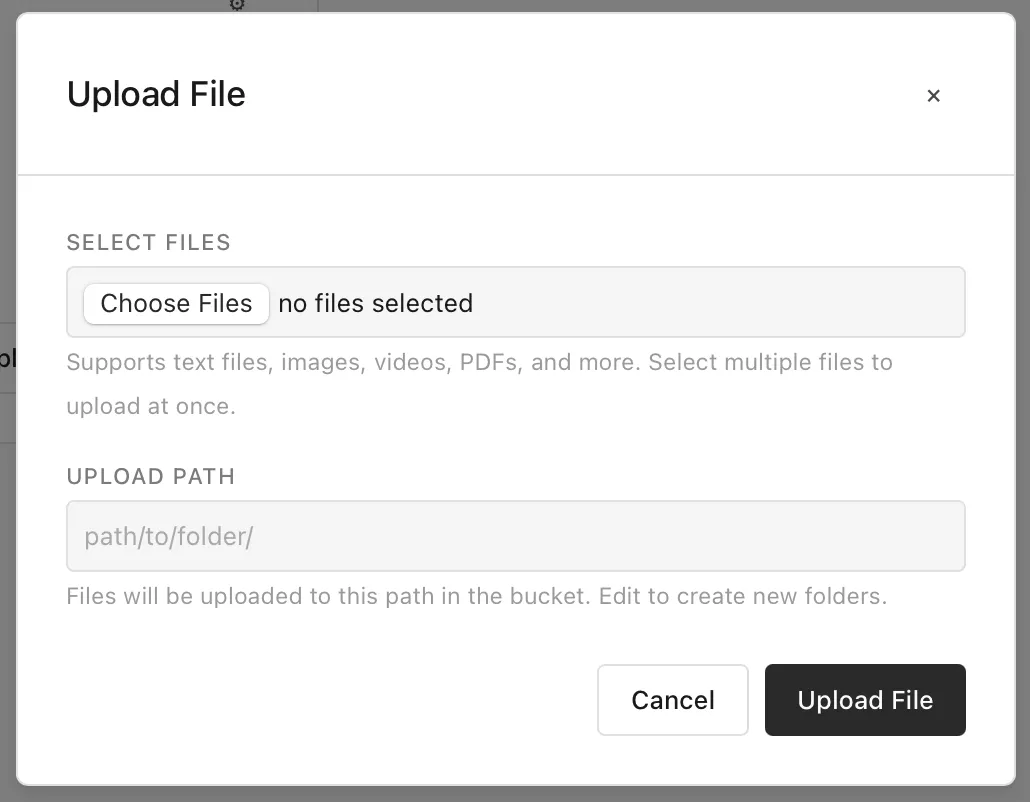
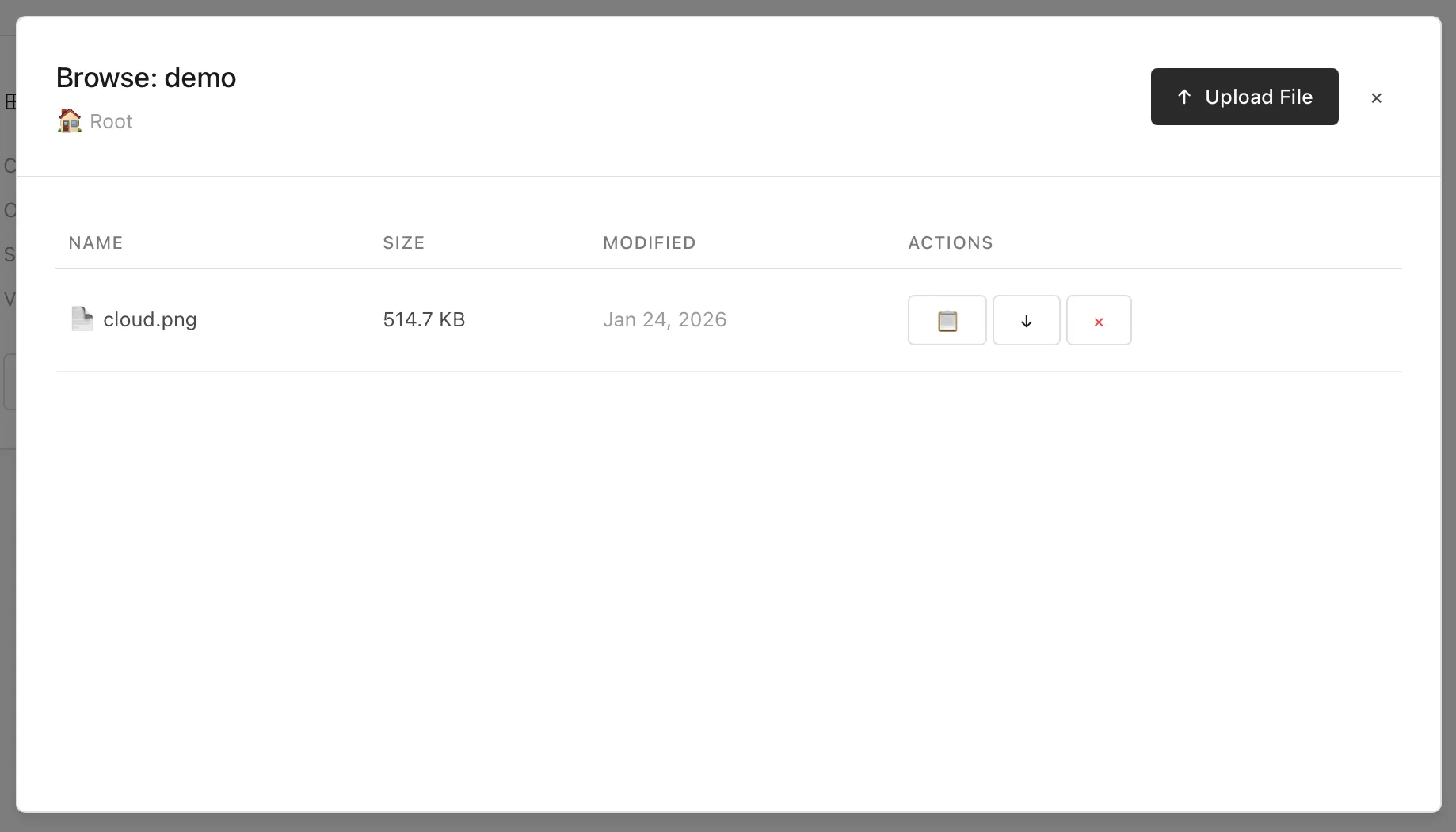
Like in S3 and similar services, you can virtually navigate the paths of a bucket. From here you can also copy a link (if public), download, and delete a file (aka. “object”) from the bucket.
Storage is managed through the HTTP API at /storage/* endpoints.
List Buckets
Section titled “List Buckets”GET /storage/bucketsReturns all storage buckets:
{ "buckets": ["my-bucket-1", "my-bucket-2", "my-bucket-3"]}Create Bucket
Section titled “Create Bucket”POST /storage/buckets/{bucket}Creates a new bucket with the specified name. Optionally configure public access and associate with a context:
{ "public": false, "context": "my-app"}Parameters:
public(optional) - Whether the bucket should be public (default:false)context(optional) - Context name to associate this bucket with for organizational grouping
Get Bucket Statistics
Section titled “Get Bucket Statistics”GET /storage/buckets/{bucket}Returns bucket statistics:
{ "bucket": "my-bucket", "objectCount": 42, "totalSize": 1048576, "public": false}Update Bucket
Section titled “Update Bucket”PATCH /storage/buckets/{bucket}Update bucket configuration (e.g., make it public or private):
{ "public": true}Response:
{ "success": true, "bucket": "my-bucket", "public": true}Delete Bucket
Section titled “Delete Bucket”DELETE /storage/buckets/{bucket}Deletes a bucket (must be empty).
List Objects in Bucket
Section titled “List Objects in Bucket”GET /storage/buckets/{bucket}/objects?prefix=docs/Lists objects with hierarchical navigation:
{ "objects": [ { "key": "subfolder/", "size": 0, "lastModified": "2025-12-19T13:45:00.000Z", "type": "folder" }, { "key": "readme.md", "size": 5678, "lastModified": "2025-12-19T13:45:00.000Z", "type": "file" } ], "prefix": "docs/"}Prefix Filtering Examples:
- No prefix: Shows root level (files + virtual folders)
docs/: Shows immediate children under docs/docs/api/: Shows immediate children under docs/api/
Upload Object
Section titled “Upload Object”PUT /storage/buckets/{bucket}/objectsMethod 1 - JSON upload (text content):
{ "key": "documents/readme.txt", "content": "Hello, World!"}Method 2 - Binary upload with query param:
PUT /storage/buckets/{bucket}/objects?key=images/photo.jpgContent-Type: application/octet-stream
[binary data]Method 3 - Multipart form upload:
PUT /storage/buckets/{bucket}/objectsContent-Type: multipart/form-data
key: images/photo.jpgfile: [file data]Get Object
Section titled “Get Object”POST /storage/buckets/{bucket}/objectsRetrieve an object:
{ "key": "documents/readme.txt"}Response:
{ "bucket": "my-bucket", "key": "documents/readme.txt", "content": "Hello, World!"}Delete Object
Section titled “Delete Object”DELETE /storage/buckets/{bucket}/objectsDelete an object:
{ "key": "documents/readme.txt"}Storage operations using the MolnOS CLI:
# List all bucketsmolnos storage buckets
# Create bucket (private by default)molnos storage bucket create my-bucket
# Create public bucketmolnos storage bucket create my-bucket --public
# Get bucket statisticsmolnos storage bucket get my-bucket
# Update bucket (e.g., make it public)molnos storage bucket update my-bucket public=true
# Delete bucketmolnos storage bucket delete my-bucket
# List objects in bucketmolnos storage objects list my-bucket
# List objects with prefix (hierarchical navigation)molnos storage objects list my-bucket docs/
# Upload text content to objectmolnos storage object put my-bucket documents/readme.txt "Hello, World!"
# Upload file to objectmolnos storage object upload my-bucket images/photo.jpg /path/to/local/photo.jpg
# Get/download objectmolnos storage object get my-bucket documents/readme.txt
# Delete objectmolnos storage object delete my-bucket documents/readme.txtPermissions
Section titled “Permissions”Storage requires appropriate permissions to manage buckets and objects:
storage.bucket.create- Create new bucketsstorage.bucket.list- List bucketsstorage.bucket.read- View bucket statisticsstorage.bucket.update- Update bucket configuration (public/private settings)storage.bucket.delete- Delete bucketsstorage.object.write- Upload objects to bucketsstorage.object.read- Download and view objects directlystorage.object.list- List objects in bucketsstorage.object.delete- Delete objects from buckets
Fine-grained permissions can target specific buckets:
storage.bucket.list:my-bucket- List specific bucketstorage.bucket.read:my-bucket- Read statistics for specific bucketstorage.object.write:my-bucket- Write access to specific bucketstorage.object.list:my-bucket- List objects in specific bucket